基本介绍
- 反射可以在运行时动态获取变量的各种信息,比如变量的类型(type),类别(kind)
- 如果是结构体变量,还可以获取到结构体本身的信息(包括结构体的字段、方法)
- 通过反射,可以修改变量的值,可以调用关联的方法
- 使用反射,需要引入
reflect包
应用场景
- 不知道接口调用哪个函数,根据传入参数在运行时确定调用的具体接口,这种需要对函数或方法反射。
- 对结构体序列化时,如果结构体有指定Tag,也会使用到反射生成对应的字符串。
重要的函数和概念
reflect.TypeOf(变量名) 获取变量的属性,返回reflect.Type类型
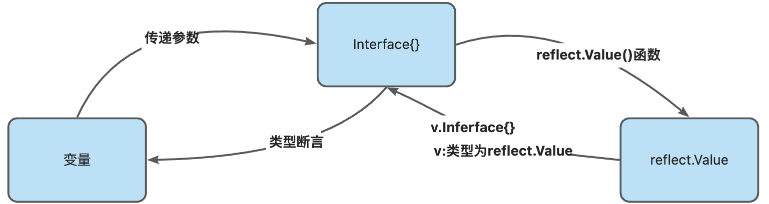
reflect.ValueOf(变量名) 获取变量的值,返回reflect.Value类型(结构体类型),通过reflect.Value,可以获取到关于该变量的很多信息。
变量、Interface{} 和reflect.Value是可以相互转换的,这点在实际开发中会经常使用到。

快速入门
案例1:演示对(基本数据类型、Interface{}、reflect.Value)进行反射的基本操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func reflectTest(b any) {
// 通过反射获取到传入的变量的type,kind,值
// 1.先获取到reflect.Type
rType := reflect.TypeOf(b)
fmt.Println("rType = ", rType) //rType = int
// 2.获取到reflect.Value
rValue := reflect.ValueOf(b)
fmt.Printf("rValue = %v, rValue Type = %T\n", rValue, rValue) //rValue = 100, rValue Type = reflect.Value
// n2 := 2 + rValue //rValue并不是真正的值,直接使用会报错:2 + rValue (mismatched types untyped int and Value)
n2 := 2 + rValue.Int() // 通过rValue.Int()获取到真正的值
fmt.Println("n2 = ", n2) //n2 = 102
// 3. 将rValue转换成interface{}
iV := rValue.Interface()
// 将interface{}通过断言转换成需要的类型
num2 := iV.(int)
fmt.Println("num2 = ", num2) //num2 = 100
}
func main() {
var num int = 100
reflectTest(num)
}
|
案例2:演示对(结构体类型、Interface{}、reflect.Value)进行反射的基本操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| func reflectTest2(b any) {
// 1.先获取到reflect.Type
rType := reflect.TypeOf(b)
fmt.Println("rType = ", rType) //rType = main.Student
// 2.获取到reflect.Value
rValue := reflect.ValueOf(b)
fmt.Printf("rValue = %v, rValue Type = %T\n", rValue, rValue) //rValue = {Joker 18}, rValue Type = reflect.Value
// 3. 将rValue转换成interface{}
iV := rValue.Interface()
// 将interface{}通过断言转换成需要的类型
stu, ok := iV.(Student)
if ok {
fmt.Printf("stu.Name = %v, stu.Age = %v\n", stu.Name, stu.Age) //stu.Name = Joker, stu.Age = 18
}
}
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int
}
func main() {
stu := Student{
Name: "Joker",
Age: 18,
}
reflectTest2(stu)
}
|
注意事项和细节说明
1、reflect.Value.Kind 获取变量的类别,返回的是一个常量。文档

2、Type是类型,Kind是类别,它们可能是相同的,也可能是不同的
Var num int = 100 num的Type是int,Kind也是int
Var sty Student stu的Type是 pkg.Student,Kind是struct
3、通过反射可以让变量在interface{}和Reflect.Value之间互相转换
4、使用反射的方式来获取变量的值(并返回对应的类型),要求数据类型匹配,比如x是int,那么就应该使用reflect.Value(x).Int()获取值,否则将会在执行时报panic
5、通过反射来修改变量,注意当使用SetXX方法来设置需要通过对应的指针类型来完成,这样才能改变传入的变量的值,通过需要使用到reflect.Value.Elem()方法

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| func reflectTest3(b any) {
rValue := reflect.ValueOf(b)
//rValue.SetInt(200) // 错误用法
rValue.Elem().SetInt(200)
}
func main() {
var num = 100
//reflectTest3(num) //如果要修改值,必须传递指针类型,否则报错:reflect.Value.SetInt using unaddressable value
reflectTest3(&num)
fmt.Println("num = ", num) //num = 200
}
|
6、reflect.Value.Elem()理解

Elem 返回接口 v 包含的值或指针 v 指向的值。如果 v 的种类不是接口或指针,它会发生panics。如果 v 为 nil,则返回零值。
1
2
3
4
5
| // rValue.Elem()用于获取指针指向变量,类似以下代码示例:
num2 := 9
var ptr *int = &num2
*ptr = 3
fmt.Println("num2 = ", num2) //num = 3
|
最佳实践
1、使用反射来遍历结构体的字段,调用结构体的方法,并获取结构体标签的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| func TestReflect01(t *testing.T) {
model := User{
Name: "Joker",
Age: 18,
}
// 获取reflect.type类型
iType := reflect.TypeOf(model)
// 获取reflect.value类型
iValue := reflect.ValueOf(model)
// 如果类型不是结构体类型,就退出
if iValue.Kind() != reflect.Struct {
t.Error("type is not struct")
return
}
// 获取结构体字段数量
num := iValue.NumField()
t.Log("num = ", num) // num = 2
// 遍历结构体字段
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
// 获取字段名需要使用reflect.Type
name := iType.Field(i).Name
t.Logf("Field[%d] name: %v, 值: %v\n", i, name, iValue.Field(i))
//获取到结构体字段的标签值,需要通过reflect.Type来获取
tagVal := iType.Field(i).Tag.Get("json")
if tagVal != "" {
t.Logf("Field[%d],Tag: %v\n", i, tagVal)
}
}
// 获取结构体方法数量
numMethod := iValue.NumMethod()
t.Log("numMethod = ", numMethod) // numMethod = 2
// 遍历结构体方法
for i := 0; i < numMethod; i++ {
// 获取方法名需要使用reflect.Type,可以看到这里获取的方法顺序是按照方法名的ASCII码顺序来的
t.Logf("Method[%d] name: %v\n", i, iType.Method(i).Name)
}
// 调用方法,需要使用reflect.Value
res := iValue.Method(0).Call(nil)
t.Log("res = ", res[0].Int())
res = iValue.Method(1).Call(nil)
t.Log("res = ", res[0].String())
params := []reflect.Value{reflect.ValueOf("yy")}
res = iValue.Method(2).Call(params)
t.Log("res = ", res[0].String())
// 可以使用方法名进行调用
res = iValue.MethodByName("GetName").Call(nil)
t.Log("res = ", res[0].String())
res = iValue.MethodByName("GetAge").Call(nil)
t.Log("res = ", res[0].Int())
res = iValue.MethodByName("Say").Call(params)
t.Log("res = ", res[0].String())
}
|
2、使用反射的方法来获取结构体的tag标签,遍历字段的值,修改字段值,调用结构体方法(要求:通过传递地址的方式完成)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| func TestReflect02(t *testing.T) {
model := &User2{
Name: "Joker",
Age: 18,
}
// 获取reflect.type类型
// 获取reflect.type类型
iType := reflect.TypeOf(model)
// 获取reflect.value类型
iValue1 := reflect.ValueOf(model)
iValue := iValue1.Elem() // 获取指针指向的值
// 如果类型不是结构体类型,就退出
if iValue.Kind() != reflect.Struct {
t.Error("type is not struct")
return
}
// 获取结构体字段数量
num := iValue.NumField()
t.Log("num = ", num) // num = 2
// 遍历结构体字段
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
// 获取字段名需要使用reflect.Type
name := iType.Elem().Field(i).Name
t.Logf("Field[%d] name: %v, 值: %v\n", i, name, iValue.Field(i))
//获取到结构体字段的标签值,需要通过reflect.Type来获取
tagVal := iType.Elem().Field(i).Tag.Get("json")
if tagVal != "" {
t.Logf("Field[%d],Tag: %v\n", i, tagVal)
}
}
// 获取结构体方法数量
numMethod := iType.NumMethod()
t.Log("numMethod = ", numMethod) // numMethod = 3
// 遍历结构体方法
for i := 0; i < numMethod; i++ {
// 获取方法名需要使用reflect.Type,可以看到这里获取的方法顺序是按照方法名的ASCII码顺序来的
t.Logf("Method[%d] name: %v\n", i, iType.Method(i).Name)
}
t.Logf("model: %v,%p\n", model, model) // model: &{Joker 18},0x1400000c0a8
iValue1.MethodByName("SetName").Call([]reflect.Value{reflect.ValueOf("yy")})
t.Log("newType = ", iValue.Field(0).String())
iValue1.MethodByName("SetAge").Call([]reflect.Value{reflect.ValueOf(20)})
t.Log("newType = ", iValue.Field(1).Int())
iValue1.MethodByName("Print").Call(nil)
t.Logf("model: %v,%p\n", model, model) // model: &{yy 20},0x1400000c0a8
}
|
3、定义了两个函数test1和test2,定义一个适配器函数用作统一处理接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| func TestReflect03(t *testing.T) {
test1 := func(v1 int, v2 int) {
t.Log("test1 :", v1, v2)
}
test2 := func(v1 int, v2 int, s string) {
t.Log("test2 :", v1, v2, s)
}
bridge := func(any interface{}, args ...interface{}) {
// 解析传递的参数值数量,并定义一个切片用于存储参数值
params := make([]reflect.Value, len(args))
// 遍历参数值,将参数值存入切片
for i, v := range args {
params[i] = reflect.ValueOf(v)
}
// 通过反射调用函数
rValue := reflect.ValueOf(any)
rValue.Call(params)
}
bridge(test1, 1, 2)
bridge(test2, 1, 2, "yy")
}
|
4、使用反射操作任意结构体类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| func TestReflect04(t *testing.T) {
var (
model *User
rValue reflect.Value
)
model = &User{}
rValue = reflect.ValueOf(model)
t.Log("reflect.ValueOf", rValue.Kind().String()) //reflect.ValueOf ptr
rValue = rValue.Elem()
t.Log("reflect.ValueOf.Elem", rValue.Kind().String()) //reflect.ValueOf.Elem struct
// 设置字段的值
rValue.FieldByName("Name").SetString("yy")
rValue.FieldByName("Age").SetInt(18)
t.Log("model", model) //model &{yy 18}
}
|
5、使用反射创建并操作结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| func TestReflect05(t *testing.T) {
var model *User
// 获取类型
iType := reflect.TypeOf(model)
t.Log("reflect.TypeOf", iType.Kind().String()) //reflect.TypeOf ptr
iType = iType.Elem() // 获取指针指向的类型
t.Log("reflect.TypeOf.Elem", iType.Kind().String()) //reflect.TypeOf.Elem struct
// 创建实例
obj := reflect.New(iType) // 创建一个指定类型的实例
t.Log("reflect.New", obj.Kind().String()) //reflect.New ptr
elem := obj.Elem() // 获取指针指向的值
// 设置字段的值
elem.FieldByName("Name").SetString("yy")
elem.FieldByName("Age").SetInt(18)
model = obj.Interface().(*User) // 将反射对象转换为接口类型
t.Log("model:", model) //model: &{yy 18}
}
|